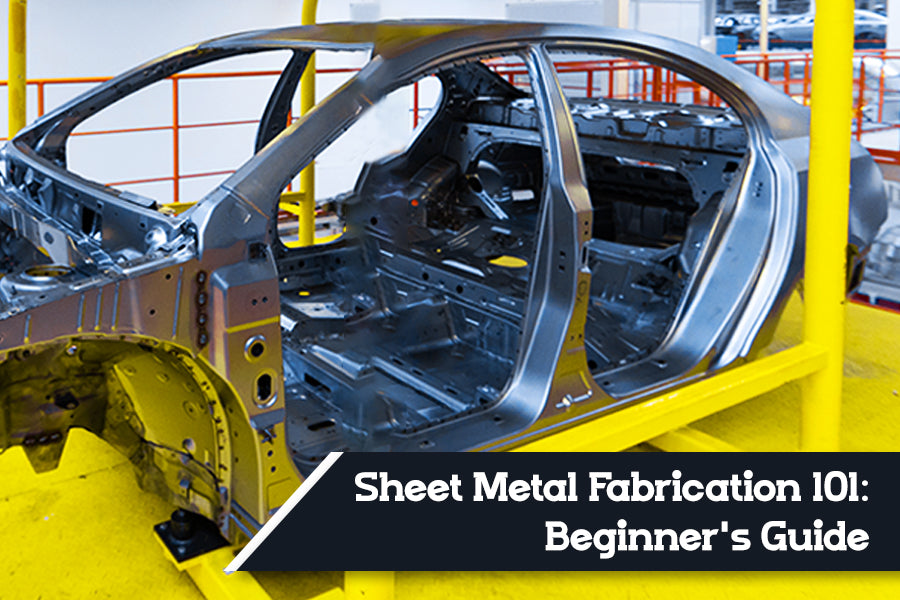
Sheet Metal Fabrication 101: A Beginner’s Guide
Have you just found your interest in Race Car Business? Are you thinking of owning a few beautiful classic Race Cars? Or do you want to keep your old cars in perfect shape?
Then you must have recently come across the term, “Sheet Metal Fabrication,” which is supposedly the reason why you are here today!
Sheet Metal Fabrication in the automotive industry is a cardinal process of producing various engine and internal/external vehicle components. It involves a vast range of processes, mechanisms, tools, and tricks that can be often confusing for both skilled experts and beginners.
So, you are not alone to stress over it!
But, having in-depth knowledge on this topic is going to help you take the best advantage of it. Although, the process of fabricating sheet metals is complicated and involves several precise requirements, knowing every detail about it can make the task easier for you.
This blog is a comprehensive custom race car Sheet Metal Fabrication guide where we have shed light on its mechanism, techniques, finishing process, pros/cons, application, and many more details.
Stay tuned with us and read till the end to learn more about the fabrication of sheet metals.
What Is Sheet Metal Fabrication?
Sheet Metal Fabrication is the procedure of turning flat sheets of steel or aluminum into composite metal products or structures by folding, cutting, punching, or assembling. It’s one of the most crucial procedures needed to build custom interiors of hand-crafted Race Cars. You can bend, cut, or stretch sheet metals into nearly any shape. It’s generally done by cutting and burning the metal.
Typically, sheet metal fabrication techniques involve transforming the various types of sheet metals into multiple parts and components. These techniques work in collaboration with other processes to manufacture the required part of the race car. As a result, it can be considered a collective forming technique instead of a single manufacturing procedure. We will be digging into each of these procedures in the below sections shortly.
This method applies to a wide range of metals, including Steel, Copper, Aluminum, Brass, and Stainless Steel. Whether it’s the race car appliances or accessories, you will get to find sheet metal fabricated products in every racing auto.
Bonus Point: Who Is A Metal Fabricator?
Metal fabricators are professionals who fabricate and mark off the structural steel and other metallic items to repair or make metal products or structures of racing cars. Sheet metal fabricators specialize in several techniques involved in the metal fabrication procedure – from initial design to final product preparation.
Sheet Metal Fabrication Guide – The Detailed Process
“What is the sheet metal fabrication process?” It’s a common question for beginners who have just become familiar with the procedure. While it’s true that the process is not simple, you can make it simple by following some easy steps. When we first started our work in this industry, we adhered to the same steps we have jotted below. Believe us; you will be able to reduce half of your burden and save yourself from committing any mistake that may cost the earth:
Step 1: Design
When designing any sheet metal part, two very crucial tips are developing an idea first and creating a draft of the design. Because of its complexity and the time-consuming activities involved, rushing the job without any proper idea or blueprint is a blunder.
-
Generating the idea
While manufacturing racing autos, sheet metal fabrication begins with an idea. This involves basic motorsports designing concepts. Do your research to put down multiple ideas roughly and accumulate all the realistic requirements for the project.
-
Making the initial blueprint
After your idea is formed, it’s time to create the first draft or the very first blueprint to determine the specifications. Prepare a 3D model of the desired product, including requirements for bend radii, wall thickness, bend allowance, and hole orientation. Once this is complete, draw every part where custom metalwork is needed. You can do it on paper or go for digital drawing as well.
Step 2: Analysis
Immediately after the idea generation, you can’t start the fabrication since you have to understand crucial details of manufacturing. So, before you begin the fabrication process, it’s important to deep dive into the manufacturing steps. A perfect manufacturability analysis can help you with that.
-
In-depth manufacturing analysis
Recheck the drawings along with other related calculations to ensure they are in line with the requirements. We recommend you follow a “Design For Manufacturing” strategy that will help you to simplify the designs and standardize the fabrication.
This way, you or the engineers will get deeper insights into how to manufacture the developed designs. After you have completed the manufacturability analysis, a final shop drawing with detailed calculations of load limitations, and stress levels are needed. The information in that drawing will allow you or the professionals to determine the ultimate sheet metal fabrication process you will implement.
Step 3: Fabrication
Now that you have a design model, a 3D blueprint, the manufacturing strategy, and an analysis, you can start the Fabrication process. In this step, you transform the flat sheets of aluminum or steel into metal products or structures through different techniques.
-
Prototype Development
To develop a desired prototype according to your draft plan and resources, adopt methods, such as cutting, punching bending, welding, and stamping. This is the step where you apply the surface finishes for improving the aesthetics of the prototype. Don’t hurry or rush as this will lead to skipping a few steps thereby, compromising the integrity and quality of the product.
-
Testing And Full Part Production
The prototype is developed and now you or the clients will have to scrutinize it to be sure that all the requirements are met. A lot of times, the testing involves evaluating their capabilities in real-life situations, such as a product demo. So it is very essential to know the key drag racing tips for winning the race. That’s why many clients even want to go for a round of Drag Race to determine whether any rework is needed. As soon as a prototype passes the testing, it will go straight into full production.
Processing Techniques – How Does Sheet Metal Fabrication Work?
Sheet metal fabrication is one of the most important steps in the customization of sports vehicles. The journey from sheet to metal product begins with CAD engineering. After the successful completion of making the models, every part passes through a set of necessary sheet metal fabrication procedures.
There is a plethora of processing techniques involved that are performed to obtain the desired results. However, the fundamentals are always the same. These techniques define the fabrication works of sheet metal in the auto racing sector. We have broken down the types of sheet metal fabrication below into the following steps:
-
Laser Cutting
Thermal cutting or Laser cutting is the best option for melting and vaporizing metal sheets, thereby giving the finest cut-edge. It’s a very precise cutting method that guarantees desired results. Use a high-powered laser guided by Computer Numerical Control (CNC) to cut the metal surface with a laser beam. Undoubtedly, with this procedure, you can give a clean and accurate cut with maximum fidelity.
-
Mechanical Cutting
Mechanical custom sheet metal cutting or Shearing is the most common procedure for fabricating sheet metals. Place the sheet between two sharp-edged blades. The top blade comes down on the sheet which lies on the bottom edge. In this way, you can easily cut the sheet from both the lower and upper edges. When it comes to race car manufacturing or any other form of industrial application, it’s the best-suited procedure.
-
Stamping
By stamping, you can transform the flat metal blanks into multiple shapes. Using a tool and die, change the metal’s basic form by using shear pressure. This procedure revolves around bending, punching, embossing, coining, and flanging. Copper alloys such as bronze, nickel, and brass are some of the most ideal materials for metal stamping. This process works well on the cold metal sheet.
-
Bending
It’s the technique of bending the metal sheets, which is another pivotal step in sheet metal fabrication. To carry out the sheet metal bending process, use rolling machines, press brakes, and a series of other equipment such as tools and dies. These sets of equipment generate standard shapes like V-bends or U-bends.
No matter how simple it looks to the untrained eyes, it’s a complex process that requires skilled manufacturers. It’s because of the “spring back”, which is the term used when metal tries to regain its original structure after bending. To avoid this custom sheet metal fabrication issue, you need to over-bend the metal part so that it springs back at the desired angles.
The two most common bending procedures to choose from are – Metal Brake and Form Bending.
In the case of a Metal Brake, place one end of the metal sheet in an opening, known as a Gate while pressing the other end with a bar. This pressure produces the desired bends on the segment inside the gate. In form bending, you have to bend the sheet with a hammer. Position the sheet on an edge and blow it with a hammer to bend it along the edge.
-
Punching
Make holes in the metal sheet using a punch-and-die method. These materials exert a shear force to puncture and indent the metal sheet. The die then collects and accumulates the scrap materials created in and around the perforations.
-
Welding
Welding is one of the final stages in sheet metal fabrication where you integrate the metal pieces to form a single part. A broad range of welding techniques you can use includes TIG, MIG, and stick welding. It depends on the type of joint, the thickness, the type of material you want, and the parameter of the sheets.
With each of these, you can fuse the metal by melting their edges thereby creating a robust metallurgical bond between these pieces. MIG welding is the most common type of welding. In this process, you create an arc with a welding gun between an electrode wire and the metal surface. The arc dissolves both metals, resulting in a weld pool carrying the molten metal sheet and the electrode.
-
Shrinking
Heat shrinks the sheet metals to get rid of the surface deformations and obtain a smooth surface once you have bent it. You need to use a high-powered torch to treat the deformations. The heat emitted from the torch stretches the metal surface initially, which eventually shrinks after cooling. In this way, the smoothness of the surface is improved.
In the sports car market, Shrinker machines are growing in popularity day by day. They automate the shrinking process using mechanical force.
-
Stretching
Stretching is another widely used procedure of fabricating sheet metals which goes in the opposite direction of the shrinking process. The surface of the metal sheet changes under the stretching process. For best results, use a Stretch Press Machine to form the sheet metal in several ways. This equipment securely grips the material on both sides with its gripping jaw and then pulls the sheet forcefully to stretch and expand it.
Hydraulic and pneumatic piston power the jaws, which act accordingly taking into account the amount of stretch needed.
-
Finishing
This is the final stage of the sheet metal fabrication procedure. No matter, how much effort you have put into the overall process, “Finishing Says It All”. A premium-quality finishing at the end preserves the metal from a wide range of erosive effects like Corrosion and abrasion.
To make the metal last longer, you must pick the most accurate finishing technique, and one such option is Sandblasting. Propel sand as well as other abrasive particles on the metal surface at high pressure. This technique of abrasive blasting will smoothen, sharpen, and clean the hard surface accordingly.
Other than this, metal coating, polishing, and buff polishing are also some effective and durable custom sheet metal finishes in the sports car industry.
Sheet Metal Fabrication Tools
The motorsport industry has been extremely benefited from Metal Fabrication. This procedure involves using several tools and supplies which enable you to achieve specific designs on the sheet metals and give a car the desired look.
With the continuous innovation of the industry especially in the domain of metal parts of automotive, understanding which tools you need is going to make your job “gliding smooth.” That being said, we have jotted down a compiled checklist below of the tools and equipment you require in this regard:
- Throat less Shear
- Angle Grinder
- Planishing Hammer
- Corner Notcher
- Flange and Punch Tool
- Shrinker and Stretcher
- Cleco Fasteners
- Hole drillers
- Multi-Press
- Sheet Metal
- Wire cutters
- CAD Design software
- Laser Cutters
- Prototyping technology
- Robotic welders
- CMM Technology
- Powder coating plant
- Folding machinery such as automated panel benders, robotic folders, and manual press brakes.
Types of Sheet Metal Surface Finish To Select
Surface finishing sheet metal is critical for building sports car parts, especially, when they are visible such as Body Panels, Hinges, Seat Rails, Seat Belt Buckles, Most Brackets, Roll Cages, Bonnets, and many others. Even internal parts such as Turbo Kits undergo this metal shaping so that they can perform faster, thereby showing how turbo kits work. Applying the right finish to the parts after cutting and processing helps you carve out the exact look and feel you want before installation.
Learn about these 7 most common surface finishing options to bring your sheet metal parts to the next level. Make sure to check out the pros and cons too, to pick the best one that satisfies your needs.
1. Bead Blasting
Bead-blasting is the most in-demand and standard finishing process for fabricated sheet metals. You have to use compressed air to shoot a flush of tiny erosive particles like sand or glass at the metal surface.
These tiny abrasive beads give a perfectly smooth finish with visually appealing matte textures. It’s best suitable for parts made of aluminum sheets that want to give exceptional visual quality. Go for this one if you are finishing floorings or cabinets.
Pros
We have mentioned the pros of Bead Blasting below. Take a quick look:
- It’s a long-lasting metal finish.
- The process is environment-friendly.
- The sand or glass beads are non-reactive.
- Bead blasting is a safe method for brass, aluminum, and stainless steel.
Cons
We have mentioned the cons of Bead Blasting below. Take a quick look:
- If you have budget constraints, this finish may not be ideal.
- The sheet metal fabricator needs to take high precautionary measures.
- It’s not a fast-curing solution.
2. Anodizing
Anodizing is another most in-vogue surface sheet metal finish procedure which gives a decorative and corrosion-resistant surface. It’s an electromechanical process that converts the top layer into oxide making it highly durable. For sports car interiors and mechanical parts’ finishes, Anodizing is a common coating process.
In this procedure, give the sheet metal part an acid electrolyte bath and then expose it to an electric current. These result in the conversion of the part’s surface into a fully-integrated acidic oxide layer.
You will find 3 variations in Anodizing:
- Type I: Chromic acid creates a thin yet extremely corrosion-resistant coating.
- Type II: Sulfuric acid produces a long-lasting and decay-resistant finish.
- Type III: It gives a thick, wear-proof, and corrosion-proof thick metallic finish.
Pros
We have mentioned the pros of Anodizing below. Take a quick look:
- Excellent corrosion and abrasion-proof properties.
- The final product is UV stable.
- No risk of fading, chalking, or failure is involved.
- Offers a variety of sheet metal finishes.
Cons
We have mentioned the pros of Anodizing below. Take a quick look:
- There are very few compatible materials.
- Replicating consistency between the batches is difficult.
- For a smaller volume of material, it’s a truly expensive solution.
3. Powder Coating
It’s an aesthetic sheet metal finishing process where you will spray powdered paint onto the material surface. The next step involves baking the paint bonds to the upper layer of the sheet metal creating a wear-resistant strong layer. If you compare it with conventional painting techniques, Powder coating is a superior choice.
While manufacturing race car parts, you need a range of different hues, sheens, and textures to meet your brand requirements. A Powder coating can help you achieve these during the sheet metal fabrication procedure.
Pros
We have mentioned the pros of Powder Coating below. Take a quick look:
- Unmatchable resistance to abrasion.
- Say Goodbye to fading, chalking, and adhesion failure.
- Makes the end product less flammable and non-toxic.
- A long-lasting and economical finishing choice.
Cons
We have mentioned the pros of Powder Coating below. Take a quick look:
- It can go out of your budget.
- Mixing powders won’t help to achieve new colors.
4. Electroplating
Don’t you want to bear the mess related to chemical plating during building interior components for a high-performance sports car? Try Electroplating or Electrodeposition instead! Apply a layer of substrate metal to the sheet metal surface by placing both of them inside an electrolyte. Through electric conduction, these two metals create a strong bond.
Pros
We have mentioned the pros of Electroplating below. Take a quick look:
- Prevents chipping or corrosion of the metals.
- Comparatively hassle-free than Chemical plating.
- Gives a great sheen to the component that will manufacture.
Cons
We have mentioned the cons of Electroplating below. Take a quick look:
- The waste generated poses a health risk to the environment.
- For complex or large sports automotive projects, it can be costly enough.
- It’s a time-consuming sheet metal finishing approach.
5. Electropolishing
By electropolishing, you can create a shiny and smooth surface finish on a metal part with ease. This procedure reduces the cleaning time, optimizes the corrosion-prevention power, removes debris, and eliminates inconsistencies on the metal surface. Electropolishing gives a tailor-fit finish, especially to the car bonnets.
Pros
We have mentioned the pros of Electropolishing below. Take a quick look:
- Gives an improved surface finish.
- Ease of cleaning.
- Lustrous appearance.
- Decreased product adhesion.
Cons
We have mentioned the cons of Electropolishing below. Take a quick look:
- It doesn’t remove the major surface defects.
- The fumes and vapors are fatal for the human respiratory system.
- The multiphase alloys may get roughened.
6. Buff Polishing
Clean and smoothen the sheet metal surfaces of high-performance sports cars at the same time with Buff Polishing. Doing this correctly enables you to remove a series of defects like etching, oxidation, and multiple small scratches. This boosts the gleam of a car and keeps it in tip-top shape.
Pros
We have mentioned the pros of Buff Polishing below. Take a quick look:
- Buffing doesn’t take much time.
- There is no requirement for stripping.
- Gives a better surface finish.
Cons
We have mentioned the cons of Buff Polishing below. Take a quick look:
- The operational costs are a bit toward the higher end.
- You need to clean the car rigorously after buffing.
- It’s a task that professionals can only do.
7. Phosphate Coating
Phosphate coating, also known as Phosphatization, is the treatment of the racing car’s metal body using Phosphoric acid. This produces a thin adhering layer with strong corrosion resistance and adhesion properties. The coating you are going to apply is composed of iron, manganese, or zinc phosphates which give an end product with a gray or black appearance.
Pros
We have mentioned the pros of Phosphate Coating below. Take a quick look:
- High durability.
- It has anti-galling properties.
- Better friction resistance.
- Improved adhesion.
Cons
We have mentioned the cons of Phosphate Coating below. Take a quick look:
- Applying one coating after another takes time.
- If you want a shiny finish, it’s not the right choice.
Tips To Select The Right Sheet Metal Finishing Process
Metal finishing lies at the heart of automotive metalworking. It limits corrosion, reduces friction, increases solderability, strengthens the substrate, and provides paint adhesion. As a result, finding the right protective material for metals is necessary to help them last longer and perform better.
Since there are so many different types and techniques of sheet metal finishes, it might be a bit complicated to choose from. In case you are struggling hard to pick the right sheet metal finish, here is a set of tips and tricks we presented to enable you to find one.
1. Cost
It’s one of the most fundamental factors that influence your decision on the type of sheet metal finish to use. It’s best to explore all the options available from different price ranges before choosing the ultimate one. For instance, Anodizing is highly expensive but it delivers unbelievably good results.
On the contrary Powder Coating is another technique that is not as effective as Anodization. However, it’s a cheaper choice. Therefore, you should take into account both cost and quality to get unique results.
2. Turnaround Time
Another important factor to take into account in this regard is production speed. If you have a narrow turnaround time, go for quick-drying finishing material. Oppositely, if you have enough time in your hand, you can choose a slow-drying yet powerful solution. Ensuring equilibrium in between quality concerning the production time is therefore mandatory.
3. Coating Thickness
Coating thickness varies from one sheet metal finish to another. When analyzing multiple finishes at the same time, you will be able to observe a trend. Here is a sample list of coating thickness of 3 types of finishing solutions:
- Anodization finish creates a thickness from 0.5 µm to 150 µm depending.
- Electroplating produces 5 µm to 25 µm thickness.
- Powder coating’s thickness ranges from 35 µm to 200 µm.
It’s on you to determine what type of thickness you want the material to have. This depends on which sports car parts you are aiming to manufacture.
4. The Type of Material
What fining procedure you will adopt largely depends on the type of material you are working with. Certain finishing processes are compatible only with certain materials. For example, Titanium or Aluminum Is best for a successful Anodizing finish. Furthermore, based on the hardness properties of different materials, you can use either an abrasive solution, such as bead blasting, or a gentler solution, such as powder coating.
5. Uses
Sheet metal finishes are preferred by so many race car manufacturers including us mainly for functional or aesthetic reasons. Every finishing solution we discussed above is the best fit for any aesthetic function to some specific degree. In addition, they are also ideal for functional usage to different degrees. For example, stainless steel finishes give a better timeless look although aluminum finishes work pretty well functionally and aesthetically.
Choosing The Best Materials To Fabricate Sheet Metals
The selection of sheet metal materials is a ceaseless process. This means that after the selection of materials, you should validate and test them as per the product design requirements before giving the final nod.
In the sports car custom metal fabrication works, a wide range of materials are used, each having its advantages, and disadvantages. This eventually makes this selection more complicated.
To make the selection procedure a hassle-free one, consider the factors mentioned in the following checklist:
- Different external forces affect the sheet metal part.
- Cost-Constraints
- Weight Constraints
- Assembly process
- Material availability
- Corrosion resistance requirements
Below we have summarized a list of the most commonly used sheet metal fabrication materials. When we manufacture race cars, these are the materials we select from:
1. Stainless Steel
Stainless steel comes in different grades offering strong resistance to corrosion, weldability, and formability. There are non-magnetic stainless-steel materials with high chromium and nickel levels that can significantly resist formability and corrosion. There is also ferritic stainless steel which is magnetic and brilliant for decorative and non-structural applications.
Advantages
- Extremely machinable.
- Gives a corrosion-resistant finish.
- A sound combination of hardness and strength.
- Weldable enough,
- Suitable for spinning, polishing, buffing, or brazing.
Disadvantages
- An expensive option.
- Prone to chipping while processing.
- Need finishing and polishing.
- Difficult to clean.
2. Hot rolled steel
When steel passes through several roll presses at a high temperature (over 1700°F), the process produces Hot Rolled Steel easily formed. You can easily form or shape it into large pieces and use it where tolerances are not much important owing to their flexibility.
Advantages
- Great flexibility
- It’s a cheaper option.
- Great mechanical performance.
- The cooling process prevents internal stresses.
- Can give various forms and shapes.
Disadvantages
- Rough and uneven surface.
- Lesser tolerance than cold-rolled steel.
- Less formability.
- Unstable mechanical performance.
- Needs a thorough surface finish.
3. Cold rolled steel
Cold Rolled Steel is the Hot Rolled Steel that goes through an extra step of the rolling process at normal room temperature. During fabrication, if you need materials with better tolerances, go for a cold-rolled finish. They have an excellent finish.
Advantages
- Stronger and harder than hot rolled steel.
- Easy to process.
- Less spring-back.
- A good option for creating square shapes with true edges.
- Steady mechanical performance.
Disadvantages
- Expensive than hot-rolled steel.
- Available only up to 3 mm thickness.
4. Pre-plated steel
Pre-plated steels belong to the category of Galvanized Sheet metal materials. They have a rust-protective coating which gives them better prevention from natural decay. Without any second thought, you can use this material for sheet metal assembly because of its high ductility.
Advantages
- It’s a cost-effective option.
- The metal plating makes the material shinier and immune to rust, abrasion, and corrosion.
- The “plating” layer adds a visual appeal.
Disadvantages
- A lot of waste is generated, which is harmful to the environment if disposed of.
- Pre-plating a material is a time-consuming process.
5. Aluminum
Another most sought-after choice for manufacturing purposes in the Sports Vehicle sector is Aluminum. It is characterized by a desired strength-to-weight ratio that meets a lot of application requirements. Because of its fantastic corrosion resistance property, you can use it to form and process effortlessly.
Advantages
- Superb heat conductivity.
- Impressive workability, machinability, and weldability.
- Lighter than iron, copper, brass, and steel.
- Ensures a durable, low-maintenance finish.
Disadvantages
- Costlier than steel.
- It’s not a suitable option where weight and strength are primary concerns.
6. Copper/Brass
While brass is super easy to work with since its zinc content is quite low, copper materials are coated with corrosion-proof oxide layers. If you want an elegant look in your Race car parts and accessories, both of these are two fitted options.
Advantages
- Copper has antimicrobial properties.
- Ductile and malleable.
- Wonderful corrosion resistance.
- Amazing electrical and heat conductivity.
Disadvantages
- Expensive options to work with.
- Difficult to clean and maintain.
- They are not budget-friendly.
Considerations While Modeling Sheet Metal Fabrication
As a Motor Sports engineer, or being associated with Motorsports manufacturing, it’s very obvious to face difficulties while designing sheet metal parts. Believe us, when we started, we also have been to the same place. There are no such hard and fast thumb rules to model Sheet Metal Fabrication, as, for every project, the design will be different.
However, from our experience of working with sheet metal parts, we have jotted down a few points to consider in this automotive metal fabrication guide. Taking into account these particulars will help you create a flawless design for your project.
Check out the considerations below that are by the industry standard sheet metal manufacturing guidelines:
1. Wall thickness
Achieving an unwavering thickness is essential to produce high-quality car parts. Geometries having a thickness over 1 wall need sheet metals of assorted thicknesses. Again, doing this may cause orientation and alignment issues. What’s the result – Longer production times and inaccurate parts!!! Hence, consider the metal thickness and geometry to make sure the final product is aligned with the required standards and specifications.
2. Bend Radii
Do not forget to keep the bend radius of the metal sheet equal to its thickness. This will help you avoid fractions and distortions while manufacturing the final parts. Maintaining compatible bend radii across every component ensures desired orientation and optimum cost-effectiveness.
3. Bend allowance & deduction
Sometimes you have to add material to the original lengths of the sheet metal parts to help them get a flat pattern. This is what is called Bend allowance in the sports car industry. Furthermore, you may need to remove some material along the length of the flanges to get a flat pattern.
4. Holes & slots of orientation
These are two of the most crucial aspects to consider – no matter what kind of race car you are planning to build or refurbish. The diameter of the holes and slots should be exactly equal to the sheet metal’s thickness. Also, you should take care of the spacing of the holes and keep it reasonable. They should not be too close to the material’s edge.
5. K Factor
If you don’t consider the K Factor, you will miss out on a very critical parameter. It determines the neutral axis to material thickness ratio although the value is not always. Rather it keeps changing based on the physical properties of the materials involved in the sheet metal fabrication process. Understand the K factor thoroughly to achieve precise bends and cuts in the sheet metal elements.
What Are The Applications Of Sheet Metal Fabrication In The Automotive Industry?
The automotive industry is the most noteworthy recipient of the custom sheet metal fabrication technique. Its popularity dates back to the 19th century when car manufacturers used to hire talents to build or modify racing cars as well as engines.
To be very specific, in 1894, the 1st race took place where all the competing vehicles were customized in unique ways through this procedure. Nowadays, sheet metal fabrication is massively adopted in the Motor Sports world. Neither you can’t imagine the industry without it, nor, there is an alternative!
One of the most widespread applications of sheet metal fabrication in the automotive industry is redesigning the structural framework of vehicles. In addition to manufacturing new car models, many of you may love to add new settings around the primary fabrication to strengthen it.
Want to know some of the best-known applications of custom metal fabrication in the automotive sector? Check the points out below:
-
Roll Cage Fabrication
Placing a roll cage on a car is high-precision work and motorsports engineering has progressed a lot in this regard. Roll cage fabrication is a prominent implementation of sheet metal fabrication by thoroughly studying the maximum speed of a car. They have a good fit and are a quirky combination of cutting, folding, punching, and assembling along with a touch of creativity.
-
Car Customization And Modification
So many people choose to customize racing cars these days and sports car customization is the best implication of sheet metal fabrication in the automotive sector. Always consider the tastes and preferences of the person owning the vehicle. The task can be as simple as changing a part or as complicated as reworking the chassis. Sometimes, all it takes is a complete transformation including engine rearrangement to revamp the look of the car.
-
Vintage Restoration
The contemporary procedure of sheet metal fabrication is highly popular to give a modern look to vintage cars and pieces. Mostly, vintage cars have very little or no character. Hence, you have to be creative while trying to build your masterpiece. This kind of work is all about the exact skills and the right pair of eyes.
Advantages And Disadvantages Of Sheet Metal Fabrication
Custom precision sheet metal fabrication is an unbelievably valuable resource for your business. With this process, you get a product that meets your specifications. However, it has some downsides too that no one will tell you about. Experiencing them all of a sudden could disrupt your overall project plan. Hence, we want to let you know the disadvantages from our own experiences.
Let’s check out the advantages and disadvantages before you take up a project:
Advantages
- Amazing Flexibility: You may need certain functionalities in your race car model.The design options available with sheet metals are quite flexible. It leaves room for many unique solutions.
- Volume Production: The production methods like 3D printing provide faster lead times, although, this method is limited to only prototyping. Fabrication of sheet metal makes the transition from prototyping to large-scale production easily achievable. You or your team can build prototypes setting the expectations for manufacturing in larger quantities.
- Multiple Surface Finishes: The fabrication procedure offers you a variety of surface coatings that help you give a premium finish to your cars. This includes painting, plating with electricity and chemicals, powder coating, and abrasive bead blasting. Not only will the car get customized looks but also long-term protection in different conditions.
- A Range Of Materials: You can use a whole lot of metals for fabrication such as brass, aluminum, mild steel, stainless steel, hot-rolled steel, cold-rolled steel, pre-plated steel, etc. This enables you to work in a versatile way on the car designs.
- High Resistance To Corrosion: Fabricated sheet metals are less likely to get eroded because they can resist corrosion over a long time. Sports cars are subjected to an abrasive environment. It’s a metal fabrication that saves vehicles from rapid damage.
Disadvantages
- High Equipment Costs: A large portion of the cost to build a high-performing sports car goes to the cost of fabricating sheet metals. The kind of infrastructure, setup, tools, ad equipment you need for this procedure is extremely professional and big-budget.
- Complex Designs: Several complex and time-consuming steps are involved such as cutting, folding, bending, forming, assembling, and machining. After completing these, you will be able to alter a sheet metal’s shape into desired parts and pieces for auto racing vehicles.
- Long Production Process: This procedure involves some post-fabrication steps such as painting, finishing, and deburring. As a result, it’s a time-consuming project and if you are a beginner, expect a longer time than normal to deliver your client the final product.
9 Tips To Consider Before Choosing A Sheet Metal Fabrication Company
The right sheet metal fabrication company will deliver more tangible results and act as your organization’s extension. To get the full advantage of your fabrication partner, you have to hire a dedicated team with a larger workforce, and better experience, financial conditions, resources, quality, customer service, and pricing.
Having said that, picking the best metal fabrication partner is not easy; especially when there are so many emerging companies in the market. Need a reliable company for your next big project? Check out the 9 crucial points we discussed below and get ready to kickstart your project with a suitable Auto Racing metal fabricator:
1. Experience
Inquire how long has been the company in this business and also learn about the type of projects they have handled. Not necessarily, all metal fabricators have specific expertise in the automotive domain. The skills of architectural metal fabricators are completely different from that of automotive fabricators. Unless you find someone, who has relevant experience and has worked on sports car projects, continue your search.
2. Quality
No matter how small or big your project is, you will never want to compromise on quality. In addition, to the quality benchmarks, you should fix a set of in-house quality checklists and the company you will hire must pass them. Asses their quality control metrics, verify their licenses, review their sheet metal fabrication tips, and see if they are willing to commit to quality standards.
3. Equipment & Resources
The company you will choose must use the latest and most cutting-edge technological resources. This includes everything starting from inventory to launching the car model. Make sure the partner is focused on automation engineering since this will give more accuracy and reduce the expensive reworks. If your project is large, the company must be ready to make investments in new equipment.
4. Competitive Pricing
When you are in a search of an affordable and high-quality sheet metal fabrication service provider, you will receive innumerable quotes from nearby professionals. When you choose one, assess whether the pricing they offer is aligned with the other providers in the market. From the very beginning, have an estimate prepared to mention all the project costs. That way, you can avoid any last-minute hidden charges from popping up.
5. Location And Reviews
See where the sheet metal fabrication service provider is located and the areas they can serve. Simultaneously, you have to take a look at the reviews of the customers they have served in your area before. Online reviews will also work if they have a digital presence. First-hand feedback always works out when it comes to selecting an extended team. It’s advisable to select the companies near you because you can obtain support services later easily.
6. Finishing
The preliminary structure of your project is only one aspect. After it’s complete, the metal fabricator partner has to blast, paint, finish, and complete your project. Not all providers have the required facilities for finishing. Let us tell you that the fabricator you have selected may outsource the finishing of the car to another contractor. This will save a lot of money and ensure quality.
7. Workforce
The size of the company’s team is an important consideration. If your project is large and you are on a strict deadline, you need a vast and efficient crew. You may not get the final product on time if they don’t have a sufficient workforce of competent workers.
8. Facilities
Several fabricator shops may not be suitable to hand over your project to. They might advertise themselves as competent ones but if you evaluate their facilities, you won’t regard them as the “perfect fit.”
9. Customer Service
If you are searching “ Metal Fabrication Near Me, ” you are most probably concerned about the post-delivery issues for which you need robust customer service. Suppose after a few months of successfully using the cars, you or any of your clients come up with a problem. Who will you reach out to? Of course, the metal fabrication partner you hired before. So, be sure that you are choosing a company that not only supports you during the project but also after the project. Find yourself a fabricator who prioritizes your business and is flexible to meet your needs.
Redeye Race Car’s Sheet Metal Fabrication
Sheet metal fabrication is an “engineered art.” The extensive techniques involved make it possible for an adept metal fabricator to deliver a product that suits the client’s needs. Since it’s a professional service and needs a fully-resourced facility to conduct the task, it’s advisable to let a professional take care of it.
At Redeye Race Car, you can reap the amazing benefits of sheet metal manufacturing services. With our highly automated and seamless production service, you can expect lead times within 30-40 days. The swift prototyping service we offer includes a reliable manufacturing capability monitored and led by our skilled expert team.
We also ensure quality and technical assurance including authorized material certifications, quality reports, and inspection reports. Need top-notch sheet metal fabricated components? Get in touch with our team today to receive a free quote.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What Is Subtractive & Non-Subtractive Metal Fabrication?
A. Subtractive Metal Fabrication or Subtractive Manufacturing is a summative term involving cutting away pieces from a solid metal block. In the Sports Car manufacturing sector, custom metal fabrication is a subtractive process. On the other hand, Non-Subtractive metal fabrication doesn’t include the removal of any metal parts. Bending the sheet metals is a form of Non-subtractive metal fabrication.
Q2. What Is Additive Metal Fabrication?
A. Additive Metal Fabrication or metal additive manufacturing typically involves building up thin layers of material accordingly. Each layer binds with its succeeding as well as preceding layer firmly. This technology helps you produce complex shapes for Racecars that can’t be done with traditional subtractive, casting, or machining methods.
Q3. What Types Of Sheet Metal Fabrication Are There?
A. Metal fabrication is an umbrella term for various distinctive types or processes. Through these processes, you can generate custom-produced or mass-produced end products made with varieties of metals as well as their alloys – carbon steel, stainless steel, aluminum, copper, and brass. This involves cutting, forming, shearing, punching, stamping, and welding.
Q4. What Is A Metal Fabricator Job Shop?
A. A metal fabricator job shop is another term for a metal fabrication service provider equipped with professional teams and facilities. They take the projects from the clients, develop an idea, build the prototype, and send it into full production. Hiring the right job shop is crucial if you want a metal fabricator partner for your race car business.
Q5. What Is A Contract Metal Fabricator Or Manufacturer?
A. In the Sports car industry, OEMs hire Contract metal manufacturers or fabricators on a “contract” basis for producing components of parts. OEMs aren’t able to staff up pretty well. This is where contract manufacturers and fabricators help to fill the gap and take the business forward.
Q6. What Is An OEM In Metal Fabrication & Manufacturing?
A. In Automotive Metal Fabrication and manufacturing, OEM refers to an Original Equipment manufacturer.
It’s a comprehensive term that elaborates a network of complex relationships among software vendors, IT hardware vendors, hardware component makers, and channel partners like distributors and resellers.
Q7. What Are The Most Common Metal Fabrication Processes?
A. Some of the most common metal fabrication processes encompass cutting, welding, machining, shearing, forming, and punching. Each of these processes takes a particular level of skills to master on. Plus, the tools and machines needed are quite expensive. At a standard metal fabrication job shop, you will find all these processes under a single roof.
Q8. What Is CNC Machining?
A. CNC machining stands for Computerized Numerical Control Machining. It’s a digitized process where the movement of production equipment is controlled by pre-programmed code controls and software. In terms of sports automotive manufacturing, CNC machining regulates a web of complex tools and pieces of machinery which you use to design and create different prototypes.
Q9. What Is Sheet Metal Forming?
A. Sheet metal forming refers to the set of manufacturing processes where metals are shaped without changing their volume, mass, and composition. Nevertheless, it changes the properties and surfaces of the metals that are machined. As per the standard sheet metal manufacturing guidelines, you have to apply force to a metallic piece to deform the material plastically into the shape you want.
Q10. What Is CNC Cutting In Metal Fabrication?
A. CNC metal cutting is a procedure in which a wide range of tools is used to remove excess material from a part of the metal. It’s quite an easy process if you have a CNC router that helps to cut complex metal parts precisely. During metal fabrication, this process uses computerized programming codes that operate a wide range of tools to cut the soft metals and shape them.
Q11. What Are Fiber Laser & CO2 Laser Cutting In Metal Fabrication?
A. In the automobile manufacturing industry, fiber laser machines offer high accuracy along with sharp and precise cutting edge. On the contrary, CO2 laser machines are widely popular for cutting thicker plates. A Fiber Laser of 2Kqw has a narrow, focused beam that exerts 5 times more power at a specific focal point in comparison to a CO2 laser of 4kW.
Q12. What Is CNC Stamping & Pressing In Metal Fabrication?
A. The race car manufacturers are quite accustomed to the procedure of CNC Metal Stamping and Pressing.
The former involves the transformation of flat metal sheets into a wide range of shapes using implementing multiple techniques such as blanking, punching, flanging, coining, and bending. CNC pressing furthermore is characterized by CNC press brakes that are essentially machines designed to bend the sheet metal as well as its components to multiple designs and profiles.
Q13. What Is Sheet Metal Embossing?
A. In simple words, Sheet metal embossing is a specialized stamping process for producing sunken or raised patterns on sheet metals. You can achieve this process with the help of matched roller dies in a less complex way or you can also pass a metal strip or sheet between the desired patterns. Pair it with foil stamping to get a polished, 3D effect.
Q14. What Are Laser Cutting & How Do They Work?
A. Laser cutting is a thermal process of fabricating sheet metals. Here a high-powered, focused laser beam melts or vaporizes a localized segment or portion of the metallic raw materials. Through CNC and optics, the laser beam is directed at the material. After the beam gets completely perforated at a single point, it marks the beginning of the cutting process.
Q15. Which Is Better- Vertical Machining Or Horizontal Machining?
A. Horizontal CNC machines are ideal for cutting deeper grooves into the metals. However, the vertical ones are perfect to mill more parts with precision. So, both have their distinctive purposes and are the best choices in specific situations.